ChipShop microfluidic chips are manufactured in transparent thermoplastics. We summarize here the main properties of these materials so you can make the right choice for your application.
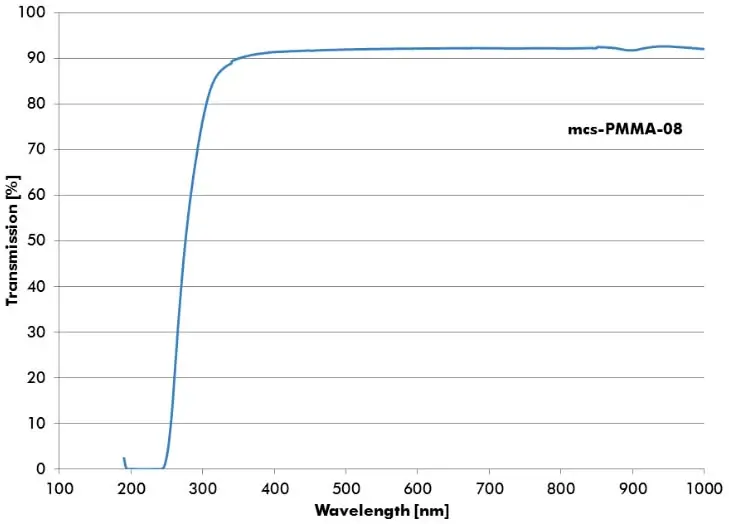
PMMA (Polymethylmetacrylate)
PMMA is a transparent thermoplastic, often used as a lightweight or shatter-resistant alternative to glass. It is sometimes called acrylic glass or Plexiglas. Chemically, it is the synthetic polymer of methyl methacrylate. PMMA is an acrylate polymer with an ester-group. This feature can be used to modify the surface chemically.
Grades:
- mcs-PMMA-08 – Tg:110°C
- mcs-foil-013 – 175 µm thickness, Tg: 113°C
PMMA can be used with:
- Aqueous Solutions including Diluted Acids and Bases
- Aldehydes
- Amines
- Oils and Fats
PMMA cannot be used with:
- Concentrated Acids and Bases
- Alcohols
- Esters
- Ketones
- Aromatics
- Halogenated Hydrocarbons
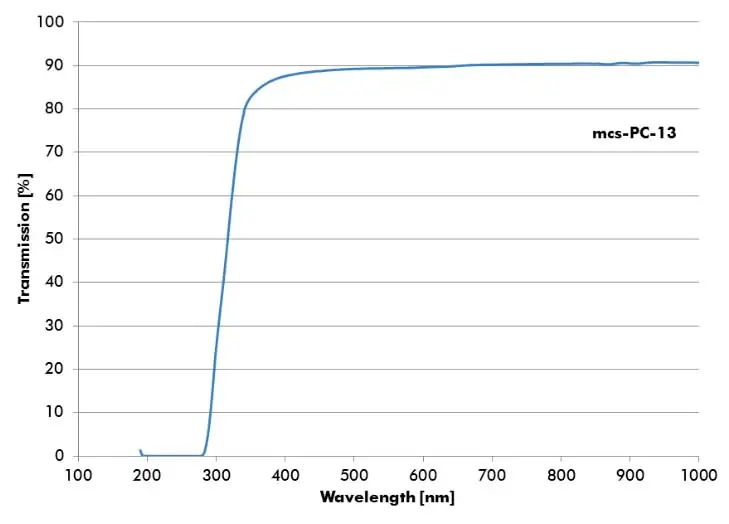
Polycarbonate (PC)
PC is a thermoplastic polymer. Compared to other materials used in microfluidics, like Zeonor or Topas, it is less hydrophobic, and therefore, the channels show a better filling behavior. It can be used for higher-temperature applications, like e.g. PCR. The drawback of this material is the relatively high intrinsic fluorescence, in particular of the available foil material, compared e.g. to Topas, Zeonor, or PMMA.
Grades:
- mcs-PC-13 – Tg:145°C
- mcs-foil-042 – Tg: 145°C
PC can be used with:
- Diluted Acids
- Oils and Fats
- Alcohols
PC cannot be used with:
- Bases
- Esters
- Ketones, Aldehydes
- Amines
- Aromatics
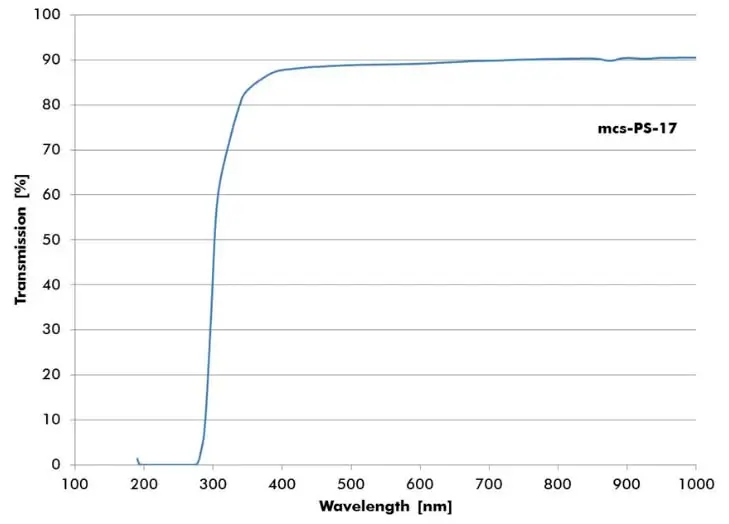
Polystyrene (PS)
PS is a thermoplastic polymer. Polystyrene (PS) is an aromatic polymer made from monomer styrene and can be rigid or foamed. Standard polystyrene is clear, hard, and brittle. The resin is very inexpensive per unit of weight. It builds a rather poor barrier to oxygen and water vapor and has a relatively low melting point. PS is one of the standard materials conventionally used in the life sciences, partially due to its relatively low price. Microtiter plates, for example, are usually made from PS.
Grades:
- mcs-PS-17 – Tg: 100°C
- mcs-foil-095 – 125µm Thickness, Tg: 100°C
PS can be used with:
- Bases
- Butyl Alcohol, Ethylene Glycol
- Organic Acids like Citric Acids, Formic Acids, Tartaric Acids
- Diluted Inorganic Acids at Lower Temperatures (except Hydrofluoric Acids)
- Mineral Oils
- Hydrogen Oxide
PS cannot be used with:
- Ketones
- Esters
- Ethers
- Halogenated Organic Reagents
- Hydrocarbons (except Mineral Oils)
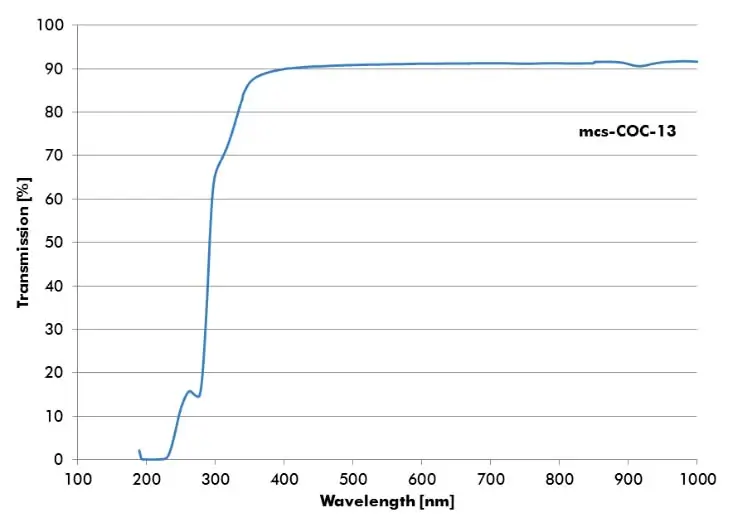
Topas (COC)
Topas is a thermoplastic polymer. It is a cyclo-olefin copolymer (COC) and completely nonpolar as well as amorphous. It has a very low permeability for water vapor and a low capacity for the absorption of water.
Grades:
- mcs-COC-13 – Tg: 142°C
- mcs-foil-011 – 140 µm thickness, Tg: 70°C
- mcs-foil-080 – 125 µm thickness, Tg: 142°C
COC can be used with:
- Aqueous Solutions including Acids and Bases
- Polar Solvents
- mcs-oil-04
- Silicone Oils
COP cannot be used with:
- Nonpolar Solvents
- Mineral Oils (Hydrocarbons)
- Fats
- Halogenated Hydrocarbons
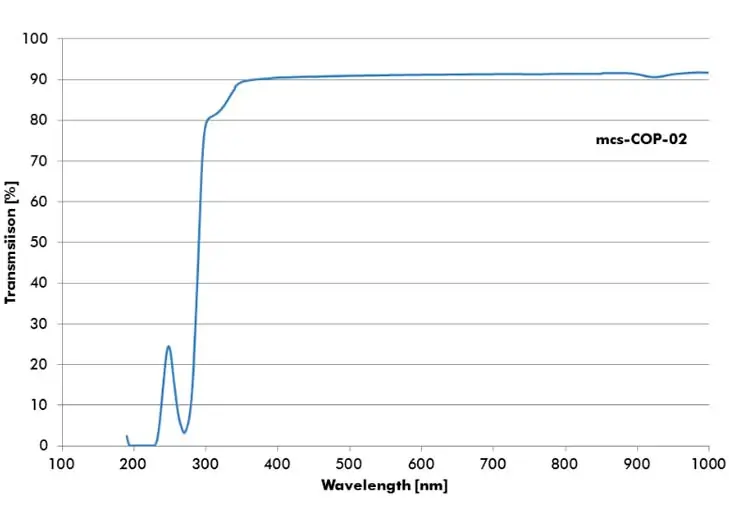
Zeonor (COP)
Zeonor is a thermoplastic polymer. It is a cyclo-olefin polymer (COP) and completely nonpolar as well as amorphous. Zeonor has a very low permeability for water vapor and a low capacity for the absorption of water.
Grades:
- mcs-COP-02 – Tg: 136°C
- mcs-foil-005 – 188 µm thickness – Tg: 136°C
COP can be used with:
- Aqueous Solutions including Acids and Bases
- Polar Solvents
- mcs-oil-04
- Silicone Oils
COP cannot be used with:
- Nonpolar Solvents
- Mineral Oils (Hydrocarbons)
- Fats
- Halogenated Hydrocarbons